MRI Quality Control
Each series in each scan undergoes quality control (QC) at the Mayo ADIR Lab. Two levels of quality control are performed:
Trained analysts manually inspect images to ensure series-specific quality, and assign a numerical grade each scan: 1-3 is acceptable and 4 is failure (unusable).
Factors that are taken into account in assigning this grade include:
Presence and severity of artifacts
(e.g., participant motion)
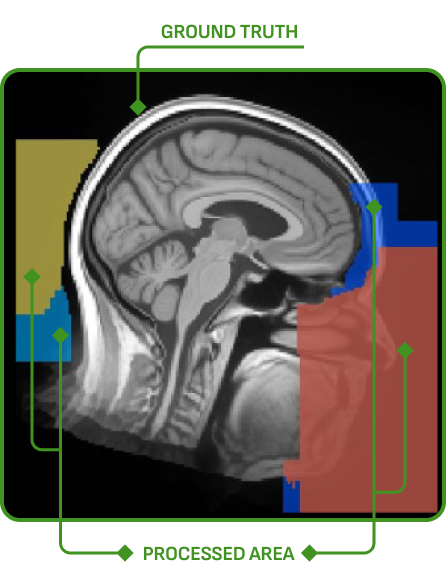
Anatomical coverage:
ensuring that the entire head was imaged
Completeness:
all slices were acquired and transmitted
Overall image quality
QC information is available for each series on LONI, and users can employ scan-level QC information as filters in preparing image collections.